Did you know that your head has more than 100,000 hairs, each of them growing for between two to six years?
If you’ve been noticing more hair in your comb, brush or pillow, it can be hella alarming but also potentially normal. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, it is normal to shed between 50-100 hairs daily. While we don’t recommend collecting and then counting them (weird), here’s some suggestions on how to figure out whether you’re experiencing normal shedding or if it’s transitioned into hair loss.
Before being able to distinguish between hair shedding and hair loss, let’s review the hair growth cycle.
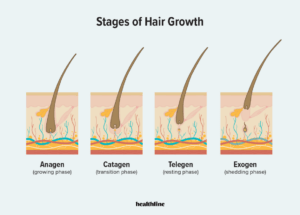
Hair Growth Cycle: A Tale In Four Phases
The normal hair growth cycle consists of four primary phases:
1. Anagen: The period during which your hair is growing and lasts between 2 to 6 years – during this phase, hair is least likely to fall out.
2. Catagen: A transitional stage that lasts between two to three weeks during which your hair stops growing.
3. Telogen: The last stage of hair growth that lasts for about three months during which the hair will naturally shed at the end of the phase.
4. Exogen: Hair falls out, and normally a new hair replaces it.
Thankfully, hair growth is not synchronized throughout the scalp to help maintain a consistent density of hair: if not we would all be bald for months at the end of the telogen phase!
A healthy scalp has a mix of hairs in varying growth phases. 85% to 90% are in anagen, 1% to 3% are in catagen and the remaining 5% to 10% are in telogen.
Understanding Hair Shedding
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, it is normal to shed 50 – 100 hairs on a daily basis. This is considered healthy and is hardly noticeable for the most part.
However, if you are noticing that you’re shedding more than normal, you could be experiencing excessive hair shedding or permanent hair loss. The medical term for excessive hair shedding is telogen effluvium.
Excessive hair shedding is common in individuals who have experienced one of the following:
- Weight loss of 20 pounds or more
- Experiencing high stress
- Recovering from a high fever or illness
- Hormonal imbalances which include estrogen, testosterone and thyroid levels being off.
An important observation, most people notice excessive shedding months after a stressful event. Doctors believe that when you have a super stressful period, your hair will proceed through the hair growth phases much faster than normal. Typically, your hair will be starting to get back to normal within six to nine months once the excessive shedding stops.
However, if this persists over time, it’s time to talk to your medical team.
Understanding Hair Loss
While hair shedding is considered normal, in true hair loss (or alopecia) the hair follicles tend to become much smaller. The medical term for this is miniaturisation. During this process, the follicles produce hairs that are smaller in diameter and often lighter in colour eventually stopping producing any hair.
Below are some of the causes of hair loss, according to Harvard:
-Drug Side Effects: Medications can have varying side effects that may include hair loss. Such medications include lithium, warfarin, heparin, and so on. Side effects from drugs often lead to sudden hair loss that affects the entire head.
-Symptoms of a medical illness: Medical illnesses can cause hair loss such as syphilis, thyroid disorders such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, or even a serious nutritional problem.
-Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disease that causes hair to fall out in small patches. The causes for the condition are currently unknown but are common in people who have other autoimmune issues.
-Traumatic Alopecia: Caused by hairdressing techniques that pull the hair, expose hair to extreme heat, or even damage the hair with chemicals.
-Androgenetic Alopecia: This is the most common type of hair loss in men, and is typically known as male pattern hair loss. It is caused by three primary factors which include male hormones, increasing age, and an inherited tendency towards baldness.
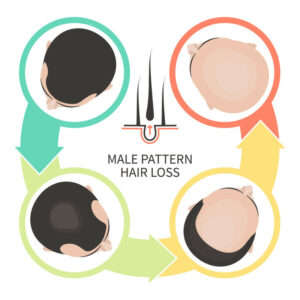
How to Spot the Difference?
Pay attention to your crown and hairline: is your hairline receding, particularly near your temples? Is is easier to see your scalp through your hair? Is the part in your hair becoming wider?
If you notice your hair thinning in the crown region or a receding hairline, it is a strong indication of early male pattern hair loss, instead of typical shedding.
The good news: there are clinically proven treatments that can halt and even reverse hair loss.
-According to the NCBI, minoxidil primarily acts by shortening the resting phase of the hair and then causes the hair to enter the growing phase. Thereby helping stop the loss of hair and promoting hair growth in patients.
-Minoxidil is available in varying concentrations with studies showing that 5% minoxidil is more effective than 2% minoxidil at treating male pattern baldness. It can take two to four months of consistent use to see results.
-Minoxidil has been clinically proven to regrow hair in nearly 62% patients.
-Finasteride is one of the most effective treatments against male pattern hair loss. It works by preventing the conversion of testosterone to DHT, preventing the hair follicles from becoming smaller and weaker.
–90% of patients saw a stop in hair loss while 65% of them saw increased hair growth.
-Topical tretinoin has been shown to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation in the epithelium, furthermore, it may also promote vascular proliferation. These factors are important in the promotion of hair growth in male pattern hair loss.
-In a study with 56 subjects with male pattern hair loss, when paired with 0.5% minoxidil, 66% of subjects had hair regrowth.
–It is thought that rosemary oil works by increasing the blood circulation to the hair follicles, providing the hair with more nutrients which can help promote growth.
-It can also help decrease dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that encourages hair loss.
-In a study conducted in 2015, researchers concluded that after a six month period of using rosemary oil, the subjects experienced a significant increase in hair count when compared to the start of the study.
Summary: there are great options to halt shedding and regrow hair, but don’t delay
Hair shedding is a common part of the hair growth cycle, however, excessive hair shedding could point to an underlying issue. For the most part, excessive hair shedding stops after 6 to 9 months.
On the other hand, hair loss tends to be ongoing until you seek treatment from medical professionals. There are various categories of hair loss: androgenetic alopecia, also commonly known as male pattern hair loss, is amongst the most common.
Trying to differentiate between hair shedding and hair loss can be tough for the untrained eye. If you suspect you are shedding excessively or facing hair loss, it’s a good idea to reach out to contact your health team who can diagnose your hair condition and prescribe treatment.

Testosterone Gel: Uses and Side Effects
Testosterone gel has emerged as a significant advancement in hormone replacement therapy, particularly for those grappling with the challenges of low testosterone levels. This topical




Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) in Canada
Suffering from low energy? Hair loss? Decreased libido? You may have low hormones. With our expert medical team you can get tested, get diagnosed, and




What is Testosterone Propionate? Uses and Side Effects
Testosterone Propionate is a synthetic form of the naturally occurring male sex hormone, testosterone. Understanding both the uses and the potential side effects of Testosterone

















 (US)
(US)



